MGI Engineering unveils TigerShark precision strike weapon with 900km range as first flight event nears
Company
Legal Links
Contact
- +44 7947 753363
- contact@skylineairporttransfers.co.uk
- 6 Walsall Street Bilston Wolverhampton WV14 0AT
© Skyline Airport Transfers. Created by![]() Beaphoenix WebDesign ltd
Beaphoenix WebDesign ltd
Popular Locations:
Birmingham: Aston, Bournville, Edgbaston, Erdington, Great Barr, Hall Green, Handsworth, Harborne, Northfield, Quinton, Soho, Sutton Coldfield, Amblecote, Brierley Hill, Coseley, Cradley, Gornal, Halesowen, Kingswinford, Lye, Netherton, Sedgley, Stourbridge, Quarry Bank, Bearwood, Blackheath, Cradley Heath, Great Bridge, Old Hill, Rowley Regis, Smethwick, Tipton, Tividale, Wednesbury, West Bromwich, Balsall Common, Bickenhill, Castle Bromwich, Chelmsley Wood, Dorridge, Elmdon, Hampton in Arden, Kingshurst, Knowle, Marston Green, Meriden, Monkspath, Hockley Heath, Shirley, Aldridge, Birchills, Bloxwich, Brownhills, Darlaston, Leamore, Palfrey, Pelsall, Pheasey, Shelfield, Streetly, Willenhall, Bilston, Blakenhall, Bushbury, Compton, Ettingshall, Heath Town, Oxley, Penn, Tettenhall, Wednesfield, Burntwood, Lichfield, Cannock, Rugeley, KIDDERMINSTER, Brierly Hill,
STOURPORT-ON-SEVERN
Coventry: Allesley, Binley, Keresley, Stoke, Tile Hill
Leicester: Abbey Rise, Ashton Green, Aylestone, Beaumont Leys, Bede Island, Belgrave, Blackfriars, Braunstone, Braunstone Frith, Bradgate Heights, Clarendon Park, Crown Hills, Dane Hills, Evington, Evington Valley, Eyres Monsell, Frog Island, Goodwood, Hamilton, Highfields, Horston Hill, Humberstone, Humberstone Garden, Kirby Frith, Knighton, Mowmacre Hill, Netherhall, Newfoundpool, New Parks, North Evington, Northfields, Rowlatts Hill, Rowley Fields, Rushey Mead, Saffron, Southfields, South Knighton, Spinney Hills, Stocking Farm, Stoneygate, St. Matthew’s, St. Mark’s, St. Peters, Thurnby Lodge, West End, West Knighton, Western Park, Woodgate
Derby: Matlock, Ripley, Ashbourne, ILKESTON, SWADLINCOTE , BURTON-ON-TRENT, BAKEWELL,
ALFRETON, BELPER, HEANOR
Telford: Market Drayton, Newport, Shifnal, Broseley, Much Wenlock
Stoke: Stoke-on-Trent, Newcastle, Leek, Uttoxeter, Stone, Stafford
Worcester: Worcester, Droitwich, Pershore, Broadway, Evesham, Malvern, Tenbury Wells
Gloucester: Gloucester, Cheltenham, Stroud, Cirencester, Tewkesbury, Badminton, Berkeley, Blakeney, Chipping Campden, Cinderford, Coleford, Drybrook, Dursley, Dymock, Fairford, Lechlade, Longhope, LydbrookLydney, Mitcheldean, Moreton-in-Marsh, Newent, Newnham, Ruardean, Stonehouse, Tetbury, Westbury-on-Severn, Wotton-under-Edge.
Nottingham: Nottingham, Sutton-in-Ashfield, Mansfield, Newark, Southwell, Grantham, Sleaford
Leicester: Leicester, Hinckley, Loughborough, Melton Mowbray, Oakham Market, Harborough, Lutterworth, Wigston, Ashby-de-la-Zouch, Ibstock, Markfield
Oxford: Oxford, Kidlington, Chipping Norton, Thame, Wallingford, Didcot, Wantage, Abingdon, Banbury, Carterton, Woodstock, Bicester, Witney, Chinnor, Watlington
Chester: Chester, Deeside, Bagillt, Buckley, Holywell, Birkenhead, Preston, Wallasey, Wirral, Neston, Ellesmere Port, Prenton
Airports we serve:
BHX: Birmingham Airport
EMA: East Midlands Airport
LHR: London Heathrow Airport
MAN: Manchester Airport
LGW: London Gatwick Airport
LTN: London Luton Airport
SOU: Southampton Airport
BRS: Bristol Airport
LPL: Liverpool John Lennon Airport
LCY: London City Airport
STN: London Stansted Airport
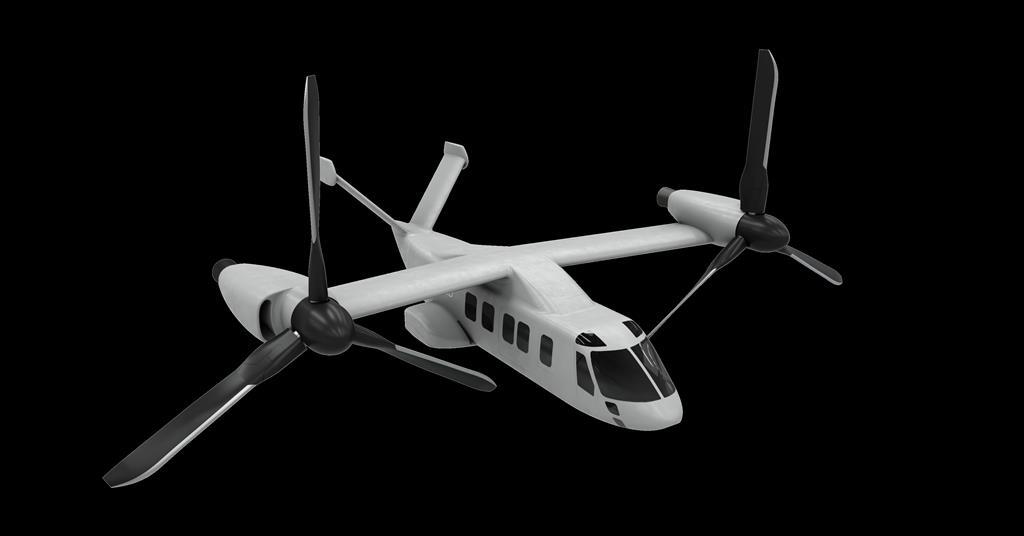


MGI Engineering has unveiled a full-scale mock-up of its TigerShark one-way effector, with the company targeting a need among militaries to rapidly field more affordable long-range precision strike weapons.
Being displayed at the DSEI exhibition in London from 9-12 September, the design has a maximum weight of 800kg (1,760lb), including a payload totalling 200-300kg.
Some 5.4m (17ft 7in) long, with a deployed wingspan of 4.3m, and powered by a pair of Argive A1100 gas turbine engines, it should have a range of 486nm (900km) when operated at a cruise speed of 351kt (650km/h), its developer says.
The weapon – which has an all-composite fuselage and 3D-printed nose section with integral avionics bay – will be launched from the ground using rocket assistance.
Those design and performance characteristics are in line with draft performance specifications laid out in September 2024 for a British Army requirement named Brakestop. That procurement activity is seeking a ground-launched weapon with a range greater than 270nm and a targeted unit cost of below £400,000 ($541,000).
“Ukraine has shown us two major points as a UK SME: they require [equipment] at low cost; and the days of trophy programmes where you’re putting multiple tens of millions and several years into developing something are gone,” MGI chief executive Mike Gascoyne told FlightGlobal at the show on 10 September.
“It needs to be low cost, and it needs to be rapidly developed. And you are going to be updating in avionics terms in weeks and months, not years.”
Gascoyne points to MGI’s motorsport-sector pedigree as evidence of its ability to match such a required pace of action. “As an F1 [Formula One] company, we are used to going racing every two weeks and putting new parts on,” he notes.
MGI has already developed its low-cost SkyShark one-way effector, which has a payload capacity of 20kg and 135nm-plus range. Applications could include electronic warfare (EW) and attack duties.
“But clearly [with] European NATO and wider there is a requirement for a heavier, longer-range system,” he says, adding: “you need to project lethality at range.”
For its TigerShark, the company is using avionics equipment, flight controller and navigation systems from specialist supplier Auterion, but has not disclosed its warhead supplier. Gascoyne notes that the design also will be able to conduct swarm operations, with a team of effectors able to share data and adjust their routing.
Meanwhile, the rapid pace of innovation in the unmanned air system sector – as evidenced by the continual process of updates required for equipment employed during the war in Ukraine – means that “When we test-fly TigerShark later this year, what it demonstrates will not be what is a production version three months later.
“That is what we as a motorsport SME bring to challenge the [industry] primes,” he says, arguing that its larger and longer-established rivals are unable to match its agility.
“We are competing against MBDA, BAE [Systems]… and we think we are going to beat them, because we are able to react and be inventive in timescales that they just can’t.”
While he declines to specifically link TigerShark to the Brakestop requirement, Gascoyne says: “We are looking to put this into production early next year – for whatever client.
“There is interest from Ukraine, and Europe – the need and the requirement is very clear.”
Also at the show, MBDA formally launched its Crossbow product: a turbojet-powered one-way effector which it says has been developed within a matter of months.
BAE, meanwhile, announced a partnering agreement between its FalconWorks innovation unit and Lockheed Martin Skunk Works, with the par initially exploring the potential to develop a “sub-1t-class” system for applications such as EW and electronic attack.
Source link
Share This:
skylinesmecher
Plan the perfect NYC Memorial Day weekend
Pack only what you need and avoid overpacking to streamline the check-in and security screening…
LA’s worst traffic areas and how to avoid them
Consider using alternative routes, such as Sepulveda Boulevard, which runs parallel to the 405 in…
Rolls-Royce remains unconvinced that open-rotor benefit outweighs integration risk
Rolls-Royce has emphasised its scepticism over the open-rotor concept, as it unveils its ducted UltraFan…
NATO next-generation rotorcraft project closes on final requirements as Boeing re-emerges as possible bidder
A project involving six NATO members aiming to develop a next-generation military helicopter has agreed…
UK Royal Air Force advances crew training capability as delayed Boeing E-7A Wedgetail nears service entry
The UK Royal Air Force (RAF) has edged closer to reinstating its lapsed airborne early…
Croatia Airlines pressured by weak revenue growth and continuing fleet-renewal costs
Croatia Airlines’ full-year losses have doubled, a situation which the carrier attributes to weak revenue…
London City consults on shallower glideslope to enable A320neo operations
London City airport is seeking to implement a shallower glideslope of 4.49° – compared with…
GTF shop visits continue to drive commercial maintenance revenues at MTU
MTU Aero Engines is expecting continuing strong demand for powerplant maintenance, with the persisting Pratt…
Draken boosts UK ‘Red Air’ service delivery with L-159E after completing first depot-level inspection
Adversary training specialist Draken has completed a first depot-level inspection on one of the Aero…
Rolls-Royce lifts Trent engine durability-improvement target
Rolls-Royce has hiked the durability improvement target for its Trent engine time-on-wing programme, raising the…
Strong aftermarket drives up Rolls-Royce aerospace profits despite dip in engine deliveries
While supply-chain issues dragged engine deliveries down last year, Rolls-Royce’s financial performance in civil aerospace…
Airbus plots European-developed version of autonomous H145M helicopter
Airbus Helicopters is actively pursuing a domestically-developed autonomous uncrewed version of its H145M light-twin for…